Dubai, in the United Arab Emirates, has a desert climate, with high temperatures and very little rainfall. Average annual rainfall in the region does not exceed 100 millimeters. The city has adopted innovative methods to artificially generate rain to increase precipitation in a region where water is a precious resource.
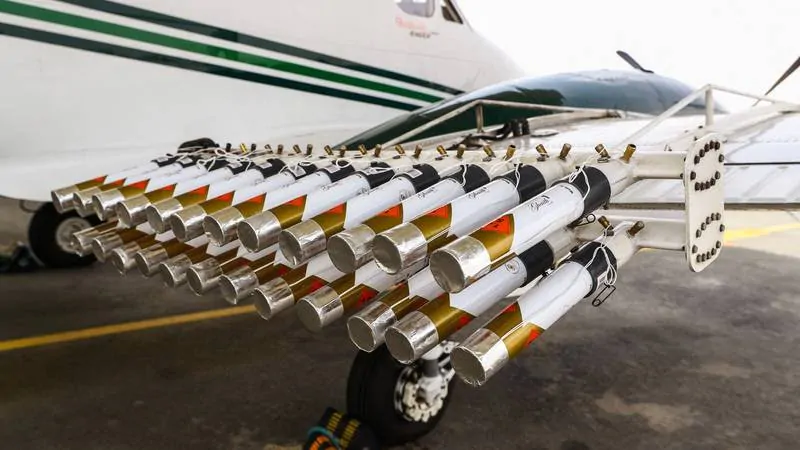

Cloud seeding is the main technique used to artificially increase rainfall. This method involves dispersing substances such as sodium chloride or silver iodide in the clouds. These particles act as condensation nuclei, encouraging the formation of droplets which, as they accumulate, become heavy enough to fall as rain.
Dubai has also begun experimenting with the use of drones equipped with electric charges to stimulate condensation in clouds. The electricity alters the structure of the water particles in the cloud, increasing the formation of rain droplets. This method is more environmentally friendly, as it does not involve the use of any chemicals.
The use of these weather modification technologies aims to increase water reserves and improve air quality by reducing dust. The city continues to invest in the research and development of new technologies, offering promising prospects for other regions facing similar climatic challenges. The aim is to position Dubai as a leader in innovative environmental technologies.